
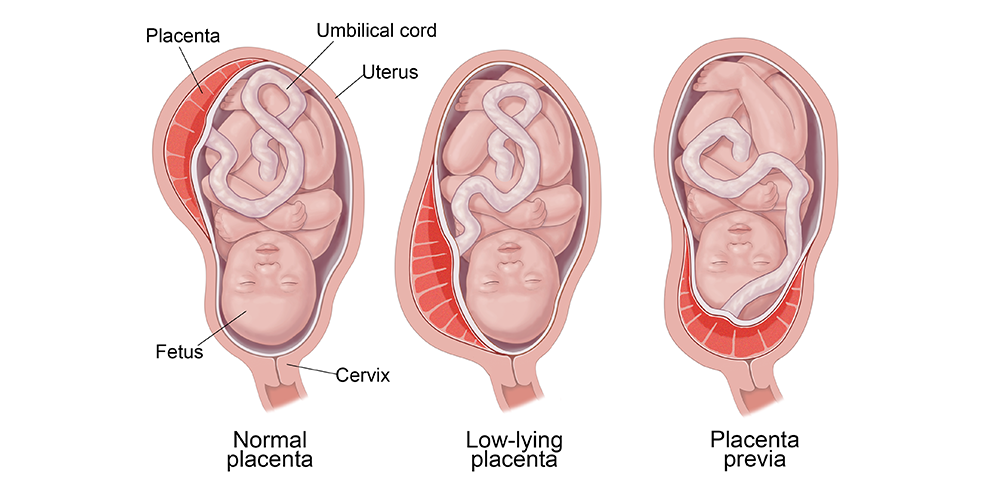
Types of placenta previa:
1️⃣ Total: When the placenta is completely cervical.
2️⃣ Upper part of the uterus.
3️⃣ Marginal: When the placenta terminates from the cervix, about 2 cm from the internal orifice of the cervix.
Signs and symptoms
Women with placenta previa often present with painless, bright red vaginal bleeding. This commonly occurs around 32 weeks of gestation, but can be as early as late mid-trimester.[8] More than half of women affected by placenta praevia (51.6%) have bleeding before delivery.[9] This bleeding often starts mildly and may increase as the area of placental separation increases. Placenta praevia should be suspected if there is bleeding after 24 weeks of gestation. Bleeding after delivery occurs in about 22% of those affected.[2]
Women may also present as a case of failure of engagement of fetal head.[10]
Cause
The exact cause of placenta previa is unknown. It is hypothesized to be related to abnormal vascularisation of the endometrium caused by scarring or atrophy from previous trauma, surgery, or infection. These factors may reduce differential growth of lower segment, resulting in less upward shift in placental position as pregnancy advances

Risk factors
The following have been identified as risk factors for placenta previa:
- Previous placenta previa (recurrence rate 4–8%), caesarean delivery, myomectomy or endometrium damage caused by D&C.
- Women who are younger than 20 are at higher risk and women older than 35 are at increasing risk as they get older.
- Women who have had previous pregnancies (multiparity), especially a large number of closely spaced pregnancies, are at higher risk due to uterine damage.
- Smoking during pregnancy; cocaine use during pregnancy
- Women with a large placentae from twins or erythroblastosis are at higher risk.
- Race is a controversial risk factor, with some studies finding that people from Asia and Africa are at higher risk and others finding no difference.
- Placental pathology (velamentous insertion, succenturiate lobes, bipartite i.e. bilobed placenta etc.)
- Baby is in an unusual position: breech (buttocks first) or transverse (lying horizontally across the womb).
Placenta previa is itself a risk factor of placenta accreta. Alcohol use during pregnancy was previously listed as a risk factor, but is discredited by this article.
Free Consultation
Email us
reservation@ivfategypt.com

5th Settlement Clinic
Address
Heliopolis - 94 El Merghany St., Cairo, Egypt
- From 6 PM to 10 PM
- Sunday
- Tuesday
- Thursday
Heliopolis Clinic
Address
Fifth Settlement - HCC Building behind the Air Hospital - Clinic 215 Cairo , Egypt
- Monday
- From 6 PM to 10 PM


