Hysteroscopy, Laparoscopy & PRP
We share your Dreams
Hysteroscopy & Laparoscopy
What is a hysteroscopy?
A hysteroscope is a thin, telescope-like device. It is inserted through the vagina into the uterus.
The hysteroscope is moved outward, and instruments with a hysteroscope are used for treatment.

Hysteroscopy & Laparoscopy

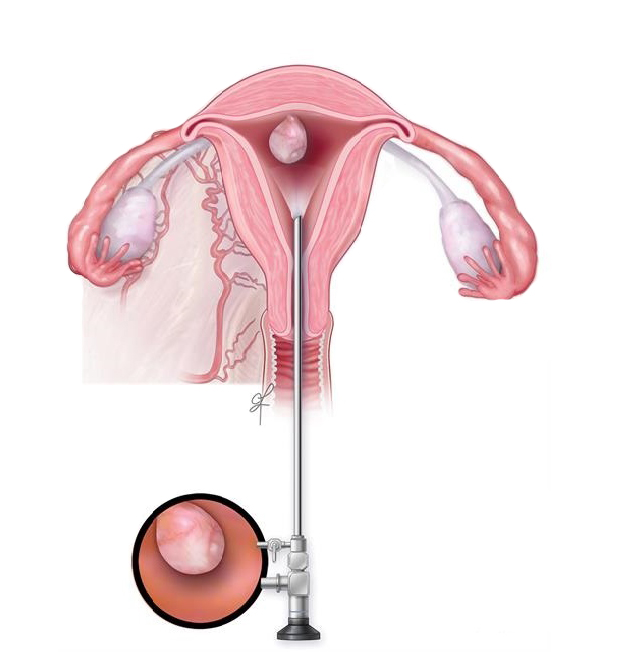
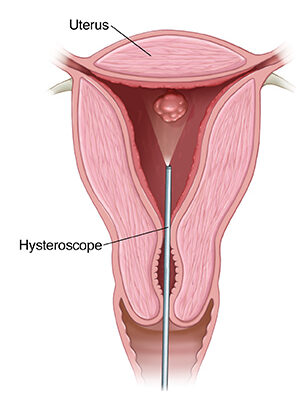
Why is a hysteroscopy performed?
One of the most common uses of a hysteroscope is to find the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding. Abnormal bleeding can mean that a woman's menstrual cycle is heavier or longer than usual or occurs less or more frequently than usual. Bleeding between periods is also abnormal. In some cases, abnormal bleeding may be caused by benign (not cancer) tumors in the uterus, such as fibroids or polyps.
Hysteroscopy is also used in the following cases:
Removal of adhesions that may occur due to infection or from diagnosing the cause of recurrent miscarriage
Hysteroscopy surgery
The doctor inserts the tube through the vagina and cervix all the way to the uterus, after that the doctor pumps carbon dioxide or saline to expand the uterus, this way the entire cavity can be seen, and possible minor adhesions parted. The duration of this hysteroscopy procedure generally ranges from five minutes to about an hour, depending on the diagnosis endoscopically made and the possible hysteroscopy surgery steps of treatment.
Uses
1- In cases of Menometrorrhagia or the abnormal loss of blood a hysteroscopy procedure can be done to find out the reasons for the bleeding as
-Bleeding can occur in cases of benign tumors, malignant tumors and polyps. According to size, type and the degree to which any of the above disturb the endometrium
- Remove of small polyps or benign tumors and evening out the endometrium lining through a hysteroscopy surgery.
2- Congenital malformations of the uterus There are different types and degrees of uterine malformations that could affect a woman’s fertility and can be removed surgically under guidance of a hysteroscope and its tools.
3- Ashermann syndrome or uterine adhesions other reasons can cause uterine adhesions; this means that the uterine walls are at different points or completely stuck to one another. Uterine adhesions are usually accompanied by painful irregular menstruations but could also lead to nonexistent menstrual cycles resulting in infertility or recurrent abortions.
Types of Hysteroscopy
1- Diagnostic hysteroscopy procedure Diagnostic hysteroscopies are done to accurately diagnose something that by medical history, symptoms or after an ultrasound sonography is suspected. It can also be done to evaluate the cervix, endometrium lining, uterine cavity and fallopian tube orifices in cases of infertility or recurrent abortion. 2- Therapeutic (operative) hysteroscopy A therapeutic or (operative) hysteroscopy is a hysteroscopy where not only the cervix, uterine cavity and fallopian tube ostia have been evaluated but where during the evaluation a deviation was found and operatively treated through hysteroscopy surgery.
IVF & Hysteroscopy
A hysteroscopy procedure like discussed earlier is a procedure that can both diagnose and treat patients. In IVF it is important to determine the state of the endometrium lining making sure there are no polyps or irregularities in the cavity in which the embryos will be returned. A small scratch in the endometrium has also showed to increase the implantation rates after Embryo Transfer (ET). Your doctor will determine whether it is useful in your case to do this and when. Many women fear doing a hysteroscopy and worry about pain, recovery time and complications. It must be said that this procedure is officially called an office hysteroscopy and could in most cases be done in the clinic without anesthesia.
Successful pregnancy after hysteroscopy
A hysteroscopy procedure has many advantages, it is a diagnostic and operative tool of treatment that is less invasive, requires less time in the hospital and has less complications than other methods. It has also proven to considerably increase pregnancy rates in IVF and ICSI cycles in general not only if it removes a polyp or fibroid that could work as an Intra Uterine Device (IUD).
Hysteroscopy & Laparoscopy
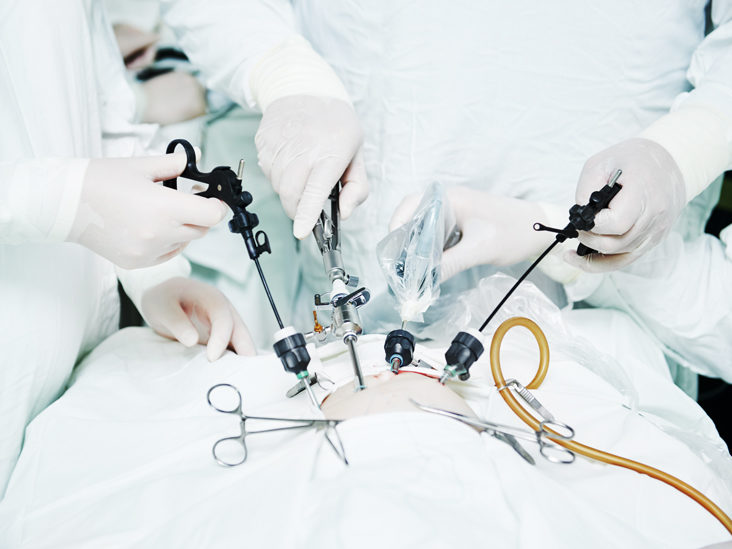
Laparoscopy
it is a simple operative procedure that in certain cases is a good alternative to open surger Hospital admission time is reduced, pain is less, operation entry wounds are much smaller and with it the scars
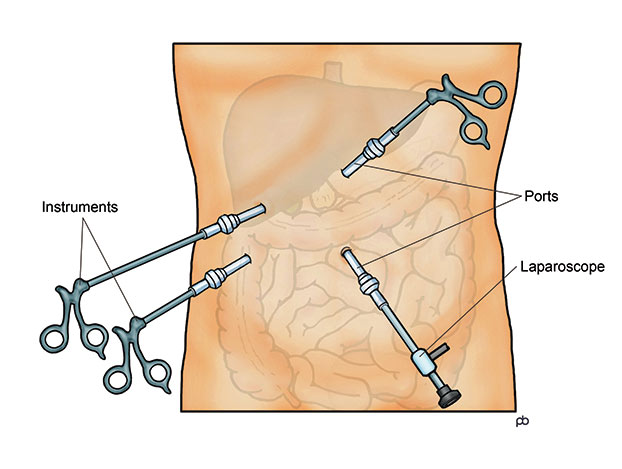
Laparoscopy Procedure
it is a surgical technique where the surgeon makes small incision cuts (1 to 4) of about 1 cm around the navel area. One of these incisions is to insert a thin tube (Trocar) through which carbon dioxide is pumped to inflate your stomach, a camera is then placed to visualize the internal abdominal organs. Depending on what the gynecological surgeon's findings are more small cuts are made through which tubes are brought in that can guide the operating tools.
What is laparoscopy used for?
The most important conditions for using Diagnostic laparoscopic surgery: Diagnosis of ovarian masses. Diagnosis of possible causes of pelvic pain. Diagnosis of abnormal masses or anomalies around uterus fallopian tubes and ovaries. Diagnostic tool in cases of infertility in women. Identify the causes of menometrorrhagia (abnormal menstrual cycle).
Operative laparoscopic surgery
During a diagnostic laparoscopy when a proper diagnosis and assessment have been made it is easy to intervene during the same session and do an operative laparoscopy. Laparoscopy is not only a diagnostic tool, but also a potential tool of treatment. Several studies show good results such as reduced pain and improved fertility rates after an operative laparoscopy. It is one of the first recommended interventions in infertile women particularly women suffering from endometriosis. However, endometriosis patients should know that their symptoms could with time return if new endometriotic spots form in the abdominal/pelvic cavity.
Treatments through operative laparoscopy
1- Operative excision of ovarian tumors, cysts & endometriosis
2- Operative excision of abnormal masses or anomalies around uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries.
3- Biopsy and evaluation of certain types of cancers, especially cancers of the reproductive system and uterine cancer. If after biopsy it is confirmed that there is cancer or a severe anomaly. Laparoscopic assessment of progression, inspection of adjacent tissues and grading is done. If laparoscopically safe, surgeries such as a hysterectomy, salpingectomy or excision of other affected tissues could be done.
Benefits of laparoscopic surgery
• Smaller incisions and thus less pain compared to open surgery.
•Shorter recovery times
•Decreased post-operative infection rates
Preparations of laparoscopy surgery
1- Take the prescribed laxatives12 hours before the procedure to empty the intestines. This, to maximize abdominal and pelvic space and to make risk of infections less
2- Do all the required bloodwork such as CBC, PT, PTT, liver and kidney functions.
3- Complete fasting for at least 8-12 hours before the procedure.
4- Inform your operating surgeon about any medication you might be taking some medications like anti-coagulants should be stopped at least 5 days before the procedure.
Aparoscopy for infertility
There are some conditions delaying pregnancy that can only with certainty be diagnosed through laparoscopy. This because you can see the affected tissues live and, on the spot, take samples for histologic and pathologic investigations. A Laparoscopy procedure plays an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis. Endometriosis can be diagnosed and endometriotic cysts and spots removed from the ovaries, pelvic & abdominal cavity and peritoneal lining
What is ovarian and endometrial PRP?
It is considered a modern method, although research and experiments began more than ten years ago, beginning with joint and muscle injections, and expanded to other fields, including nerves, cosmetic and many others, until it began to be used recently in the uterus and ovaries. Blood from the same woman is approximately 20 mm, and in the lab, white and red blood cells are filtered, and plasma and platelets are concentrated, which contain growth hormones GH, in a concentrated amount, and this may help to revive the ovaries or the endometrium.
The injection process
Takes approximately 30-40 minutes and the patient is given a nutritious drug containing a CONSCIOUS SEDATION for a short period and after the injection she remains under observation for an hour after which she goes out to practice her normal life, and this procedure is almost similar to the known and safe IVF operations for more than 40 years, the results It becomes clear within the next 3-6 months.
As for the ovary, the response is that the ovary begins to produce eggs again, and it is followed by ultrasound examination, the rise of estrogen and egg maturation. Natural pregnancy may occur, or through artificial insemination or IVF, depending on the situation. As for the endometrium, its thickness increases by more than 6 mm, and the cycle returns to normal. This technique benefits from She suffers from a lack of ovarian reserve either due to age or the so-called early menopause, or she suffers from a weak endometrium less than 6 mm, either due to a previous surgical reason or inflammation and others.
Some cases may need stimulating hormones or a dose of plasma injections for the second or third time, and here it must be emphasized that there is 50 percent that may not benefit from this experience and there will be no response. Follow-up, especially in the early stages, is very important, especially that such new technologies do not It is still under study and needs more research to become in the future one of the treatment for such difficult cases.
Book Now
Book your Visit , Your Online Consultation or Ask The Doctor
